EV Cars: Reshaping Thailand’s automotive workforce

The rise of the EV car market has been making waves in the global automotive industry, and its impact has been notably significant in Thailand, a major player in the global automotive market. Thailand’s automotive sector is one of the most important pillars of its economy, contributing significantly to the country’s GDP and employment. As the largest automobile producer in Southeast Asia, Thailand has built a robust ecosystem of vehicle manufacturing, parts production, and assembly operations. The country is actively embracing the electric vehicle (EV) revolution, and the growing popularity of EV cars is stated to have far-reaching implications for its automotive workforce.
Thailand is adopting EV cars for several compelling reasons, driven by a combination of environmental, economic, and strategic factors that align with the country’s long-term vision for sustainable growth and development. The most pressing reason is the need to address growing environmental challenges, particularly air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Thailand is committed to reducing its carbon footprint and promoting cleaner transportation solutions. Moreover, the country is grappling with severe air pollution in urban areas, which has led to heightened public health concerns. Economically, Thailand aims to maintain its position as a major player in the global automotive industry by embracing the emerging EV market. You may also browse through the best luxury EV cars in Thailand here.
The impact of electric vehicle adoption on Thailand’s automotive workforce is multifaceted, spanning areas such as job creation, job displacement, skill development, and workforce transition. We will take a look at each of these factors in detail below, showcasing how the adoption of EV cars can transform Thailand’s automotive workforce in the long run.
Impact of EV Cars on Thailand’s automotive industry
1. Job Creation

The adoption of EV cars in Thailand is expected to lead to job creation in multiple ways, as the industry expands and evolves to cater to the growing demand for electric vehicles. As the market for electric vehicles continues to grow, Thailand is likely to witness an increase in the number of EV car manufacturing and assembly plants. This will create jobs for skilled workers, technicians, and engineers who have expertise in electric vehicle technology, including battery systems, electric drivetrains, and electronic components.
The widespread adoption of EV cars will drive the demand for advanced batteries, which are a critical component of electric vehicles. The establishment of battery production facilities in Thailand will generate employment opportunities for workers with specialized skills in battery technology, materials science, and production processes.
The establishment of dedicated R&D centres in Thailand focusing on EV car technology will create jobs for local researchers, engineers, and scientists with expertise in various fields such as battery technology, power electronics, materials science, and vehicle design. These professionals will work on developing cutting-edge solutions to improve the performance, efficiency, and affordability of electric vehicles, making them more attractive to Thai consumers.
2. Job Displacement

The adoption of EV cars in Thailand is expected to cause job displacement in certain segments of the automotive workforce, as the industry undergoes a major transformation to embrace electric vehicle technology.
As the popularity of EV cars grows, the demand for traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles is likely to decline. This will impact the production and assembly of ICE vehicles, leading to job losses for workers who are specifically skilled in manufacturing, assembling, and maintaining ICE components such as engines, transmissions, and exhaust systems. EV cars typically have fewer moving parts and a more streamlined design compared to their ICE counterparts. This simplification of manufacturing processes may result in a reduced need for labour in certain areas of production, contributing to job displacement.
As the Thai government introduces policies and incentives to promote the adoption of EV cars, it is likely that resources and investments will be redirected from traditional ICE vehicle production towards the development and expansion of the electric vehicle industry. This reallocation of resources can lead to job displacement in certain areas of the automotive sector that are more reliant on ICE vehicle production.
3. Skill Development
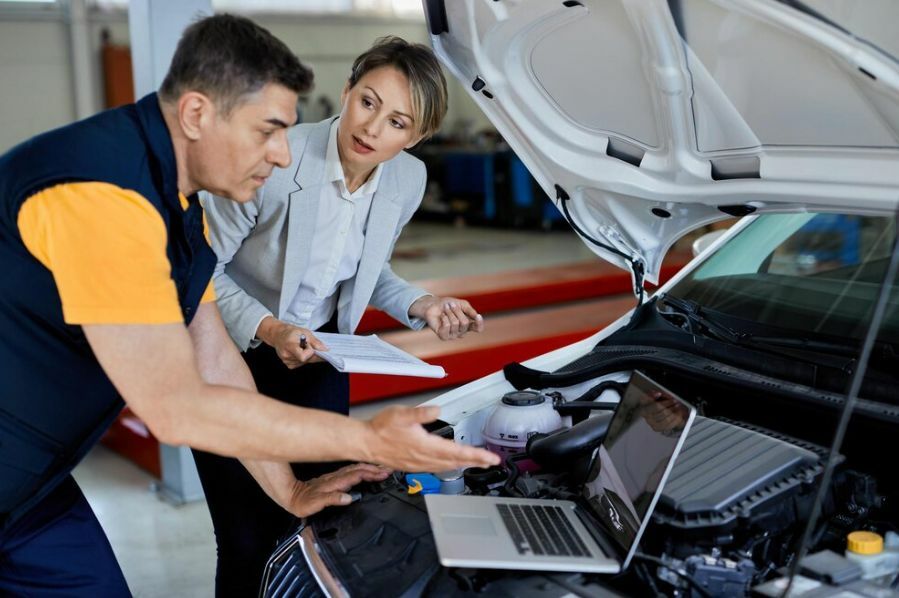

The adoption of EV cars in Thailand will drive skill development in the automotive workforce, as the industry evolves and adapts to the new technologies and processes associated with electric vehicles.
To facilitate the transition to EV car production, educational institutions and training centres in Thailand will need to develop and offer specialized courses and programs in electric vehicle technology. These programs will cover various aspects of EV engineering, such as battery systems, electric drivetrains, power electronics, and charging infrastructure, equipping the workforce with the necessary skills to excel in the EV industry.
Partnerships between automotive companies and academic institutions can help bridge the gap between industry requirements and educational offerings. Joint initiatives, such as research projects, internships, and apprenticeships, can provide valuable hands-on experience for students, helping them develop practical skills that are directly applicable to the EV car sector.
4. Workforce Transition
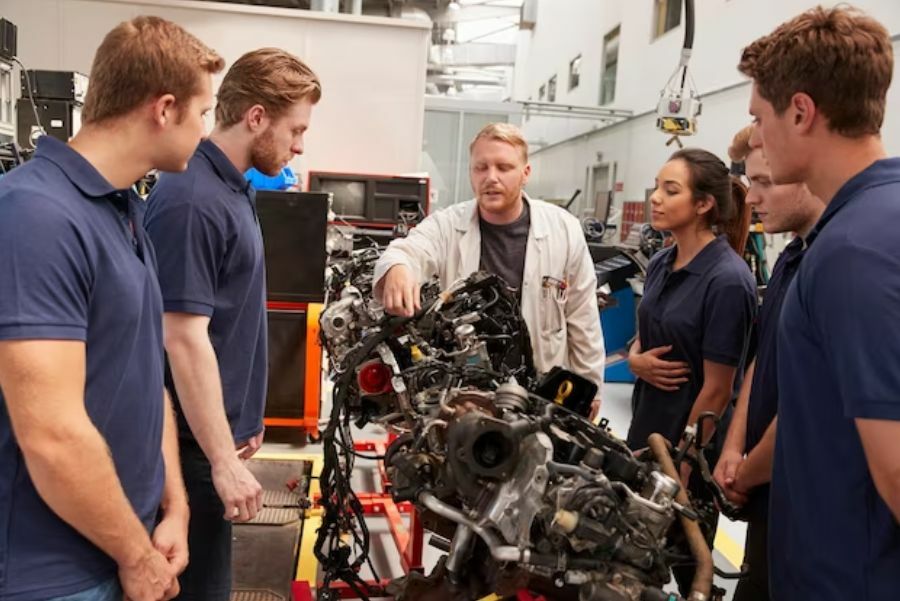

The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in Thailand is expected to have a significant impact on the country’s workforce transition. As the automotive industry shifts towards EVs, there will be changes in the skills and expertise required, and this will have implications for workers and the broader economy. One potential impact of the adoption of EVs is the creation of new jobs in the areas of battery production, electric motor manufacturing, and software development. These areas require specialized knowledge and expertise, and the growth of the EV industry will create opportunities for workers with these skills.
At the same time, the shift towards EVs is likely to lead to a decrease in demand for some of the traditional automotive jobs, such as those related to the production of internal combustion engines. This could potentially lead to job losses in the short term. However, it is possible that some workers may be able to transition to the new areas of the EV industry with retraining and upskilling.
To facilitate a smooth workforce transition, it will be important for the government, the private sector, and workers to work together to identify and address potential challenges. This may involve providing training and education programs to help workers acquire new skills, supporting job creation in emerging areas of the EV industry, and ensuring that workers are able to access the resources they need to adapt to the changing demands of the job market.
Conclusion
By investing in EV production and infrastructure, Thailand can attract international automakers, leading to job creation and economic growth. By supporting the adoption of electric vehicles, powered by domestically produced renewable energy, Thailand can achieve greater energy independence and diversify its energy sources.

On the one hand, the production of EVs requires a different set of skills and expertise compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. This means that automakers will need to retrain and upskill their workforce to adapt to the new technologies and manufacturing processes.
On the other hand, the shift towards EVs is likely to lead to a decrease in demand for some of the traditional automotive jobs, such as those related to the production of internal combustion engines. This could potentially lead to job losses in the short term.
However, it is important to note that the EV industry also presents new opportunities for job creation in areas such as battery production, software development, and electric motor manufacturing. As the EV market continues to grow, it is likely to create new jobs and transform the skills required in the automotive industry. While there may be short-term job losses in some areas, the shift towards EVs also presents opportunities for new jobs and growth in other areas. It will be important for the government, automakers, and the workforce to work together to ensure a smooth transition towards a more sustainable automotive industry.
It may also interest you to read how the Thai government has been working towards the demand for EV cars here.
Latest Thailand News
Follow The Thaiger on Google News: