What you need to know before buying an EV Car in Thailand

Looking to make the transition from a traditionally powered car to a full eclectic vehicle (EV)? The EV market in Thailand is only getting started, and more people are becoming interested in driving EV cars. Given the skyrocketing price of oil, it seems inevitable that EV cars will soon replace fossil fuel vehicles. Plus, EV cars offer a smooth driving experience and comfort. However, buying an EV car can be a challenging task if you’ve never had one before. So, if you are considering taking the plunge to EV cars this year, here are things you need to know before making your purchase.
1. Understanding battery capacity and range

“Range Anxiety” is a term frequently used when discussing reasons not to buy an EV car. A range refers to how far the electric car can travel on one charge. No one wants their car to run out of battery when they’re far away from a charging station. But today, EV range has improved drastically, so the so-called range anxiety is no longer a problem. Still, you’ll have to ensure that the EV car you choose has sufficient range and battery capacity for your activities. It’s good to overestimate your needs in terms of an EV’s estimated range because your mileage will vary.
A 100% EV car with a 60 to 90 kW battery, for instance, has a range of 338 to 473 kilometres on a single charge. This is a mid-range battery and might be sufficient if you don’t cover too much distance on average daily. However, if you feel like it’s not enough for you, it’s best to purchase an EV car with larger batteries. While they may be more expensive, you’ll get longer distances on a single charge. On that matter, you should also consider a vehicle’s capability to support chargers with greater power so that the battery can be fully charged more quickly.
2. Charging time of the battery

The time it takes to charge an EV car depends on the type of the car, the size of the battery, and the speed of the charging point. It can take as fast as 30 minutes and as long as 16 hours. The bigger the batter of the car and the slower the charging point, the longer it takes to charge from empty to full. In general, charging using an express charging station (DC charging) generally takes 40 to 60 minutes, a quick EV charger takes 3 to 4 hours, and a conventional home charging (AC) takes 12 to 16 hours. Charging a typical EV car with a 60 kWh battery might take about 8 hours from empty to full using a 7 kW charging point.
3. Maintenance of EV Car

Many people believe that EVs don’t need maintenance since they are powered by a motor rather than a fuel engine. This couldn’t be further from the truth. While EVs don’t need an oil change and rarely cause fussy problems, they still need maintenance. However, it’s not as expensive and less time-consuming than a traditional car. On average, the maintenance fee for an EV car is 50% less than a petrol car.
Still, although the maintenance fee is cheaper, it’s important to keep in mind that repairs for EVs tend to be more expensive. The auto parts needed to repair an EV car can cost a lot more than traditional cars. For instance, the battery change fee for Tesla can cost around 162,000 to 220,000 Baht.
4. Calculating the overall cost of fuel

EVs usually have higher upfront purchase prices, but owners can save a lot on fuel expenses. Of course, electricity has its own costs, but when we compare the fuel cost between an electrical charger and oil, the charging fee of oil is cheaper than filling up oil. Oil typically costs 1.50 to 3 Baht per kilometre, whereas EV charging rates typically range from 0.26 to 0.50 Baht per km.
5. Installing a charging station for the EV Car
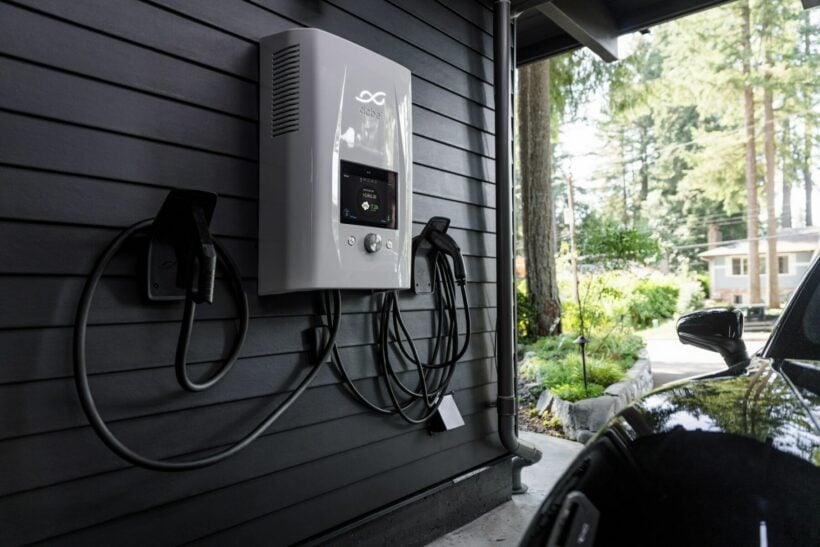

Before you buy an EV car, you need to consider whether it’s possible to install a home charger or not. The EV charging infrastructure in Thailand is currently insufficient. Even when there’s an easily reachable station from your home, it may not be compatible with your car since the brand might be different. Therefore, it’s best to install a home charging station.
To fulfil the demand for greater electrical power, you must upgrade your electric meter to at least 30Amp (A), your home’s electrical wiring to 25 square millimetres, and your Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) to 100Amp (A). 1 circuit breaker slot must also be added to the Main Distribution Board (MDB) in order to split the power when utilizing other electrical equipment at home. Additionally, Residual Current Devices (RCDs) must be installed to protect you against electric shock in the event of short circuits. You will also need an EV socket to plug the car charger adapter into the car plug of each EV series. Note that only a qualified electrician should separate and install the wiring circuits of the home charging point for EVs due to safety concerns.
6. After-sales service and warranty
EV cars are just entering Thailand’s market. Therefore, it’s important that you choose a trusted brand with high manufacturing standards. Keep in mind that an EV car can only be repaired in its service centre, so be sure to examine the after-sales service policy. The brand you choose should be able to offer help in case of emergency, have service centres in the country with high standards of service, and have great service coverage in regard to distance. Furthermore, look at all the terms and conditions of the warranty, especially on the EV car’s electrical system and motor.
We hope this information can help your transition from traditional to EV cars! Remember, always study the EV car details thoroughly before buying it, so you won’t have regrets later. If you need recommendations on the best electric cars to buy, check out our guide to the top 5 EV cars in Thailand.
Latest Thailand News
Follow The Thaiger on Google News: