Cannabis: A potential ally against long Covid brain inflammation

After the initial wave of Covid-19, many people continue to suffer from long-term effects. Known as post-Covid condition (PCC) or long Covid, this condition can cause a variety of symptoms, including neuroinflammation. This inflammation in the brain can lead to headaches, fatigue, insomnia, depression, and anxiety. Although there’s no specific treatment for PCC yet, a research published in the peer-reviewed Internal Journal of Molecular Sciences suggests that cannabis might help manage these symptoms due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Understanding long Covid
Post-Covid condition or Long Covid refers to the persistent symptoms following a Covid infection. These symptoms can last for weeks or even months after the initial illness. The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies PCC under ICD-10 code U09.9, reflecting the significant health challenge it poses. PCC can affect various body systems, including respiratory, cardiovascular, and neurological systems.
Neuroinflammation, characterised by inflammation in the brain, is a major component of PCC, causing various neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Cannabis compounds and their properties
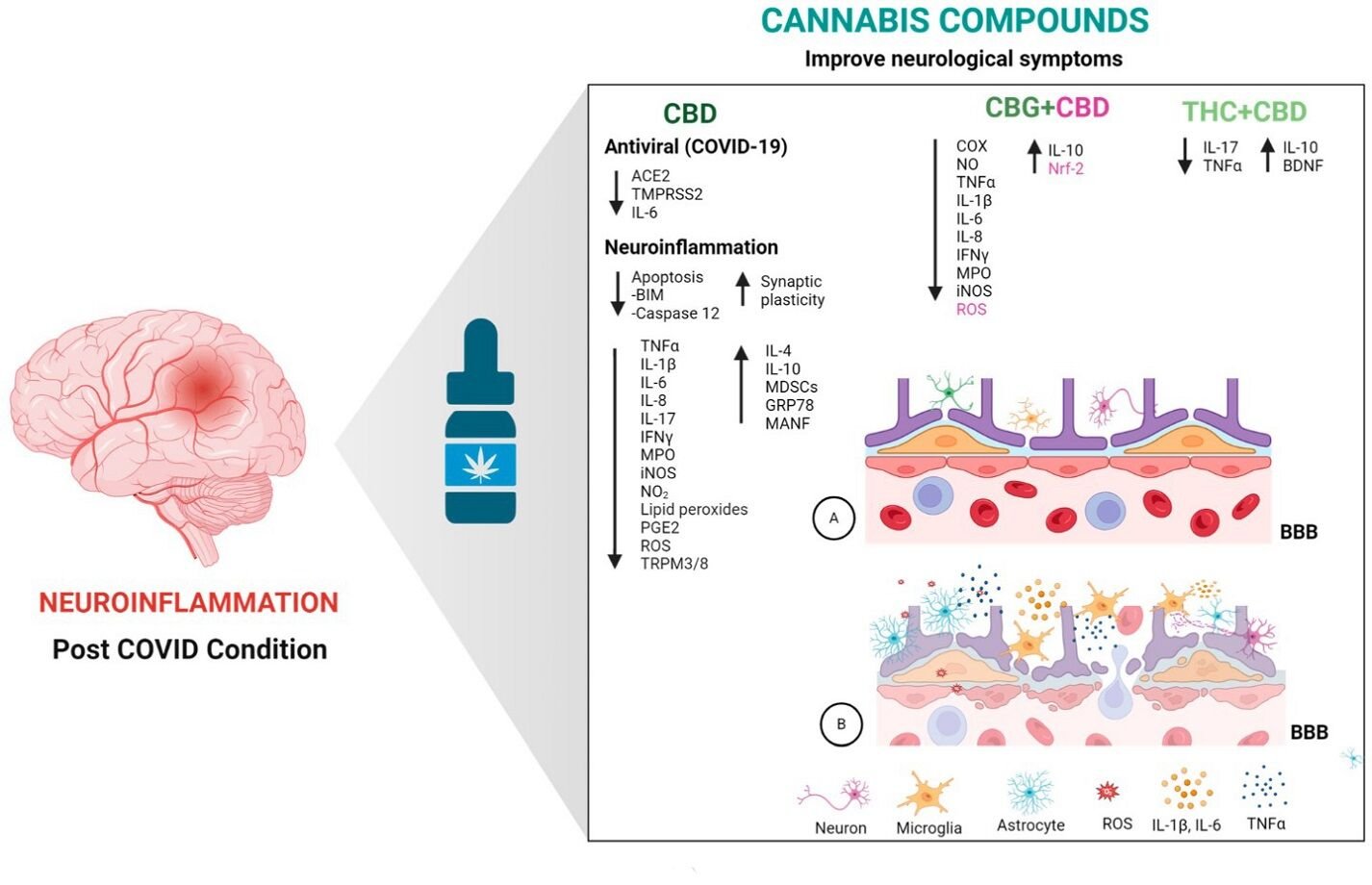
Cannabis contains several compounds, known as phytocannabinoids, which have shown promise in treating various health conditions. The most well-known of these compounds are cannabidiol (CBD), cannabigerol (CBG), and Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). These compounds have significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, making them potential candidates for treating neuroinflammation in PCC.
CBD: A potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent
CBD is a major component of cannabis with numerous health benefits. It interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which regulates various physiological processes. CBD has been shown to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, two key factors in PCC. Studies in animal models have demonstrated that CBD can significantly reduce levels of proinflammatory cytokines, which are molecules that promote inflammation. By doing so, CBD helps protect the brain from long-term damage.
CBG: The underexplored phytocannabinoid
CBG is another promising compound found in cannabis. Although less studied than CBD and THC, CBG has shown significant anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. In animal studies, CBG has been found to reduce inflammation and protect neurons from damage. This makes it a potential therapeutic agent for treating neuroinflammation in PCC.
THC: The psychoactive component with therapeutic potential
THC is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. While it is known for its mind-altering effects, THC also has medicinal properties. It interacts with cannabinoid receptors in the brain, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. However, its psychoactive effects can be a drawback, so its use needs careful consideration and regulation.
Combining cannabinoids for enhanced effects
Combining different cannabinoids may enhance their therapeutic effects. For example, a combination of CBD and THC has been shown to reduce inflammation more effectively than either compound alone. This synergy could be particularly beneficial in treating the complex symptoms of PCC. Some studies have suggested that combining CBD with other antioxidants could further enhance its effectiveness in reducing neuroinflammation.
Clinical evidence and ongoing research
Several clinical trials are exploring the potential of cannabis compounds in treating PCC. One such trial involves the use of a CBD-rich formulation to treat symptoms of long Covid. Preliminary results suggest that this formulation can significantly improve symptoms such as dyspnea (shortness of breath), anxiety, and sleep disturbances. Another trial is investigating the use of a cannabis flower formulation rich in cannabinoids and terpenes for treating PCC.
Practical considerations and future directions
While the potential of cannabis in treating PCC is promising, more research is needed to fully understand its benefits and risks. It’s essential to determine the optimal dosages and formulations for different symptoms. Additionally, regulatory considerations and potential side effects, particularly those related to THC, need careful management.
Cannabis, with its powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, holds promise as a treatment for neuroinflammation in post-Covid conditions. Compounds like CBD, CBG, and THC could help alleviate the persistent symptoms that many people experience after recovering from Covid. However, further research is necessary to validate these findings and develop safe, effective treatment protocols. As the scientific community continues to explore the therapeutic potential of cannabis, it may become a valuable tool in the fight against the long-term effects of Covid.
Latest Thailand News
Follow The Thaiger on Google News: