Phuket Finance: Using exchange traded funds
PHUKET: In today’s uncertain economy, investors are increasingly seeking diversification, safety and a secure income. Interest rates continue to hover at or near all time lows in many countries, and the continued uncertainty about the strength of the global economic recovery has made many investors extra cautious.
Nevertheless, there is one investment option available that can offer risk-adverse investors both safety and income.
What ETFs are
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) are investment funds that trade on global stock exchanges just like individual stocks.
They have been available to retail investors since 1993 in the USA and since 1999 in Europe.
Like mutual funds or unit trusts, ETFs may hold any type of asset class such as individual stocks, bonds or commodities and they can be bought or sold at the end of each trading day for their net asset value.
However, ETFs differ from many types of mutual funds or unit trusts in the sense that they usually track a specific index such as the S&P 500, the Telecommunications Services Index or the Japanese Nikkei 225.
What the benefits are
The major benefits offered by ETFs for investors include: transparency as their portfolios are priced throughout the day; diversification across an index or market, and tax efficiency – since ETFs do not need to buy and sell stock to cover investor purchases or redemptions. This also leads to lower expense ratios, since ETFs are not actively managed and have lower accounting, distribution and marketing expenses.
ETFs also come with the same features as stocks. They can be bought or sold during any part of the day as well as bought on margin or sold short. Investors can also trade ETFs using stop and limit orders in order to specify what prices they are willing to buy or sell at.
Finally, ETFs that invest in dividend paying stocks offer equity investors seeking income an additional measure of income safety as they do not rely on a single company’s dividend payout stream to generate income for investors.
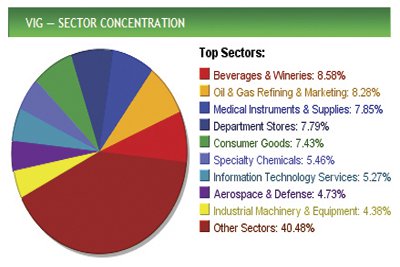
The Vanguard Dividend Appreciation ETF, for example, is designed to measure the performance of common US stocks that have a history of increasing dividends for at least ten consecutive years.
The top ten holdings are Pepsi, Procter & Gamble, McDonald’s, IBM, Johnson & Johnson, Exxon Mobil, Coca-Cola, Chevron, Wal-Mart and United Technologies (see graphic above).
The fund has a very low expense ratio of 0.25% per year, currently yields 2.2% and is up 90% from the March 2009 low.
Types of ETFs to invest in
The use of ETFs has increased exponentially as they have gained popularity with investors.
However, there are a couple of categories of ETFs that ordinary retail investors should consider adding to their investment portfolio. These ETF categories include the following:
Index ETFs:
By their very nature, most ETFs are actually an index fund as they usually track a particular stock index. This tracking can be done by owning the individual equities that make up the index.
Some examples are the iShares Emerging Markets Fund, PowerShares NASDAQ Internet Portfolio and the iShares Thailand Index Fund.
Bond ETFs:
For fixed income investors, investing in bond ETFs will offer certain advantages as they can be less risky than owning an individual bond plus investors have the ability to profit during bear market downturns or recessionary times.
Commodity ETFs:
This category of ETFs will invest in commodities, which may include precious metals, such as gold or silver. However, investors need to be aware that commodity ETFs are generally not regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), although they may in fact be subject to regulation by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission and they need to fully understand how such funds attempt to replicate the performance of a particular commodity. This is because they may be invested in futures or other exotic investment vehicles.
Currency ETFs:
These types of ETFs are total return investment products where an investor will gain access to FX (foreign exchange) spot rates and local institutional interest rates for a particular country or region. Hence, investors can profit from higher interest rates or currency fluctuations between countries.
In addition to the above ETF categories, new and more exotic ETF products, such as actively-managed diverse ETFs and leveraged ETFs, have been introduced in recent years.
Before considering these new types of ETFs as investments, investors need to fully understand that new ETF products may be subject to additional risks, which traditional ETFs are not subject to.
ETF Benefits:
Low expense ratios; tax efficiency; portfolio diversification; transparency; easy to buy and sell; same features as ordinary stock eg: limit orders, options, and stop loss orders.
Conclusion:
Investing in ETFs can be beneficial for investors seeking diversification, safety and a more secure income. However, investors need to remember that ETFs are still equity investments and hence, they can be impacted by market volatility.
Therefore, if you are thinking of investing in ETFs, be sure to consult a qualified financial advisor who can advise you on how to select the right ETF investments that will fit into your current investment portfolio and match your particular investment needs.
Don Freeman is President of Freeman Capital Management, a registered investment Advisor with the US Securities Exchange Commission (SEC), based in Phuket, Thailand. He has over 15 years experience and provides personal financial planning and wealth management to expatriates. Specializing in UK and US pension transfers. Tel: 089-970-5795 or email: freemancapital@gmail.com.
— Don Freeman
Latest Thailand News
Follow The Thaiger on Google News:


























