How to detect and prevent phishing attacks
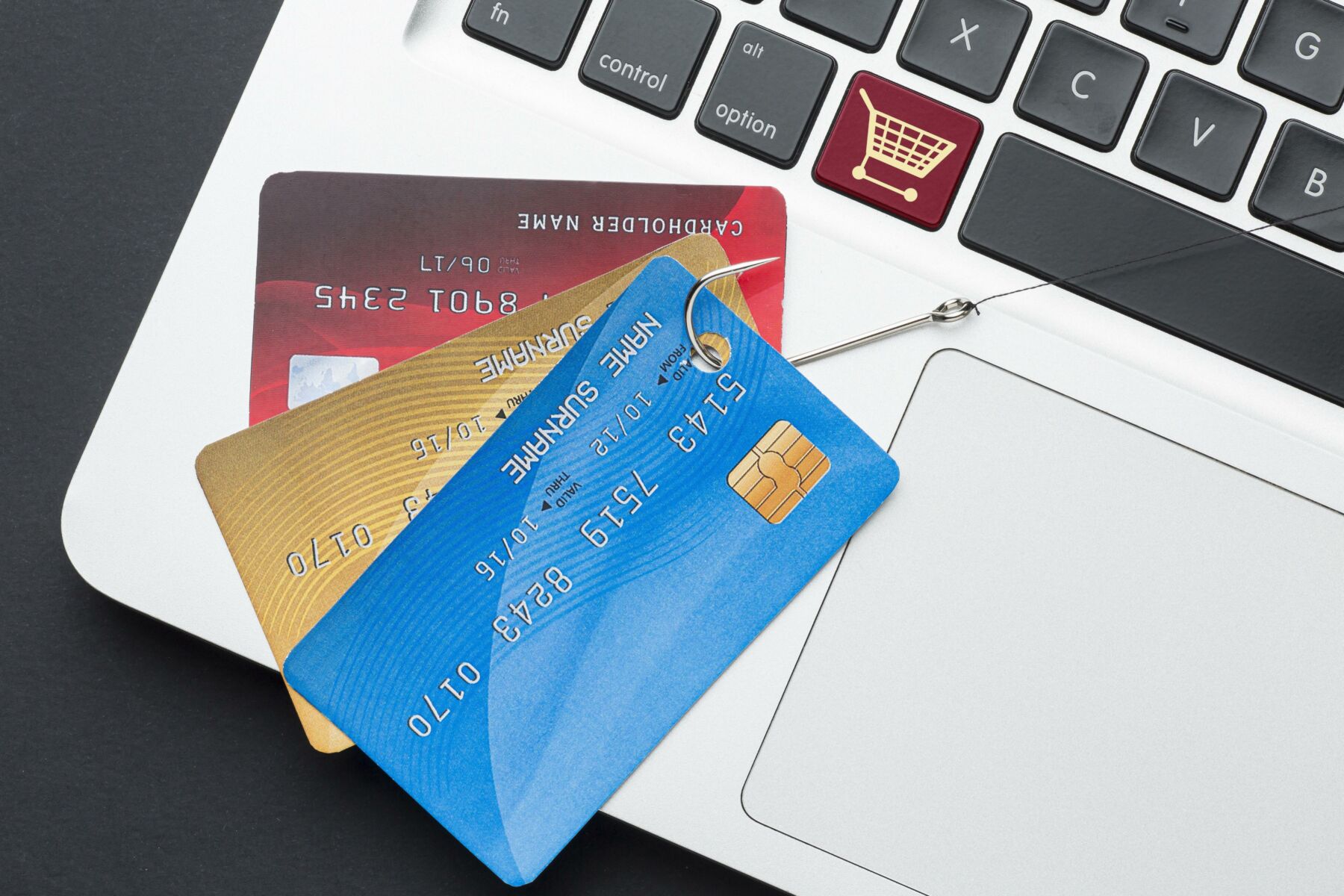

One of the worst feelings is realizing you got scammed. Phishing attacks are a common threat in the digital age, targeting individuals and organizations to steal sensitive information. Understanding and recognizing these attacks is crucial for safeguarding personal and financial data. This guide will help you understand phishing attacks, identify their common types and characteristics, and implement effective strategies to prevent them.
Comprehending phishing attacks
Definition of phishing
What is phishing? Phishing is a cyber-attack method where attackers deceive individuals into providing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity. These attacks typically occur through email, social media, phone calls, or fake websites. The primary goal of phishing is to gain unauthorized access to valuable data, which can then be used for identity theft, financial fraud, or further cyber-attacks. Phishing attacks exploit human psychology, using tactics like urgency, fear, or curiosity to compel victims to act without thinking. Although phishing and fishing are not directly related, ‘phishing’ is a play on the word ‘fishing’ as you are being baited like fish. However, after this guide, you will not take the bait anymore!
Common types of phishing
- Email phishing: The most common form, where attackers send fraudulent emails that appear to be from legitimate sources, tricking recipients into clicking on malicious links or providing personal information.
- Spear phishing: A targeted form of phishing where attackers customize their messages to a specific individual or organization, often using personal information to appear credible.
- Whaling: Similar to spear phishing but targets high-profile individuals like executives or public figures, aiming to steal sensitive corporate information.
- Smishing and vishing: Phishing attacks are conducted via SMS (smishing) or voice calls (vishing), where attackers trick victims into revealing personal information or installing malware.
- Clone phishing: This involves duplicating a legitimate email and modifying its content to include malicious links or attachments.

Principal characteristics of phishing electronic mail
Phishing emails often exhibit distinct characteristics that can help you identify them. One common trait is the use of generic greetings, such as ‘Dear Customer’ instead of personalizing with the recipient’s name. This lack of personalization is a red flag, as legitimate companies usually address you by your name. Another hallmark of phishing emails is urgency and threats. These messages create a sense of urgency or fear, urging immediate action to avoid negative consequences. For example, an email might claim that your account will be suspended unless you verify your information immediately. Although you may receive some authentic emails, be sure to always check the format and tone of the email.
Suspicious links and attachments are also telltale signs of phishing emails. These emails may contain links to fake websites or malicious attachments that install malware on the recipient’s device. Always hover over links to check their actual destination before clicking. Additionally, spoofed email addresses are common in phishing attacks. The sender’s email address might closely resemble a legitimate one but with slight variations, such as using a different domain or substituting similar-looking characters. Poor grammar and spelling are also prevalent in phishing emails. Many phishing emails contain noticeable errors, which can be a clear indicator of their illegitimacy.
Red flags in websites and social media
Phishing attacks are not limited to emails; they can also occur on websites and social media platforms. When browsing websites, look out for unusual URLs. Check for misspellings or unusual domain names in URLs, as legitimate sites usually have straightforward URLs that match the brand. Ensuring the website uses HTTPS and has a valid SSL certificate, indicated by a padlock icon in the address bar, is another crucial step. Be cautious of websites that prompt for personal information through pop-up forms, as these can be a tactic to steal your data.
On social media, beware of unsolicited messages that contain links or requests for personal information. Suspicious social media messages from unknown contacts or accounts that seem unusual should be treated with caution. Phishing attackers often create fake profiles or hack legitimate ones to spread malicious links.

Effective strategies to prevent phishing
Preventing phishing attacks requires a combination of awareness, technology, and best practices. Education and awareness are fundamental. Regularly train employees and individuals about the latest phishing tactics and how to recognize them. Knowledgeable users are less likely to fall for phishing scams. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is another effective measure. MFA adds an extra layer of security, requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access. This makes it harder for attackers to gain access even if they have obtained login credentials.
Email filtering tools are essential for detecting and blocking phishing emails before they reach the inbox. These tools use advanced algorithms to identify and quarantine suspicious emails. Always verify requests for sensitive information through a different communication channel, such as a phone call. Legitimate companies will understand and support your caution. Keeping software and systems up-to-date is also crucial. Regular updates protect against known vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
Reporting and responding to phishing attacks
If you suspect a phishing attempt, immediate action is necessary. Report phishing attempts to your IT department or the appropriate authorities. Many organizations have dedicated teams to handle such reports. Delete suspicious emails without opening them, clicking links, or downloading attachments. This minimizes the risk of inadvertently installing malware. Regularly monitor your accounts for any unauthorized activity. Early detection of suspicious transactions can prevent further damage. Lastly, using reliable security tools, such as antivirus and anti-malware software, can detect and block malicious activities.
Phishing attacks are a significant threat in the digital world, but by understanding their characteristics and implementing preventative measures, you can protect yourself and your organization. Don’t be ashamed if you are a victim of a phishing attack because from now on, stay vigilant, educate yourself and others, and use security tools to safeguard against these malicious attempts. Being proactive and informed is the best defence against phishing attacks.
Latest Thailand News
Follow The Thaiger on Google News: