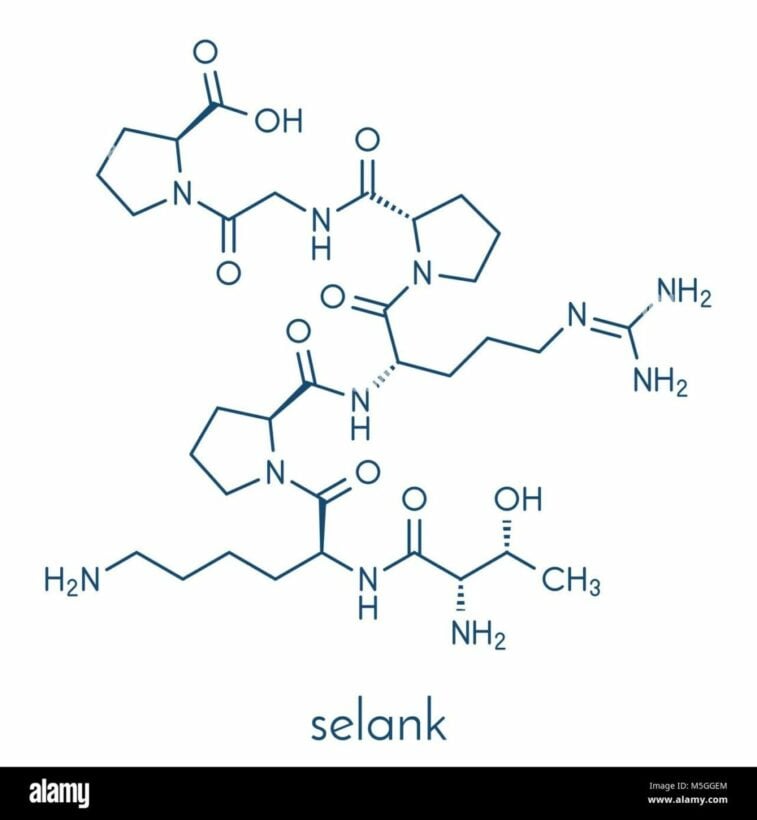
Exploring Selank peptide in infection research

Researchers have examined the synthetic peptide Selank for possible impacts on the immune system. In this piece, we examine how Selank may affect infections. It has been postulated that Selank may be able to modify immunological responses, improve antiviral activity, and impact inflammatory processes. These theories and the function of the peptide in infection control need further investigation.
The heptapeptide Selank is synthesised from the naturally occurring tetrapeptide tuftsin. Since it may have immunomodulatory and neuromodulatory impacts, it has been the focus of several preclinical investigations. With an eye on its possible processes and functions, this paper analyses the ramifications of Selank’s possible impacts on infections.

Immunity
The primary mechanisms by which Selank is thought to exert its immunomodulatory impacts are by modulating immune cell activity and cytokine production. Studies suggest that the peptide may regulate the activity of immune cells like macrophages and T cells and increase the production of certain cytokines important in antiviral defence.
Cytokines
Research suggests that Selank may affect the levels of interferons, especially interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), which are vital for antiviral immunity. In a hypothetical scenario, Selank may boost the organism’s capacity to fight viral infections by increasing the production of IFN-γ. Cytokine synthesis-related signal transduction pathway modification may mediate this impact.
Activity of Immune Cells
Additionally, Selank may influence the function of different types of immune cells. For example, it has been hypothesised to boost macrophage phagocytic activity, which improves pathogen clearance. Selank might also affect how T cells work, meaning more cytotoxic T lymphocytes—the ones the organism needs to eliminate infections—and more of them.
Viral Inhibition
Researchers are especially curious about the peptide because of its possible antiviral impacts. By disrupting viral replication pathways, Selank may directly combat viruses. Many believe that Selank can potentially reduce viral replication by altering the conditions within host cells in a way that is less favourable to the spread of specific viruses.
Disruption of Virus Replication
One possible mechanism by which Selank is believed to affect the machinery of host cells is by interfering with viral reproduction. Selank seems to decrease the effectiveness of viral genome synthesis and assembly by changing the expression of genes involved in viral replication. In vitro investigations have indicated that cell cultures presented with Selank may have had a lower viral load, lending credence to this theory.
Protective Mechanisms
Investigations purport that Selank may have direct antiviral impacts and strengthen the host’s immune system’s ability to fight viruses. An upregulation of antiviral protein production, including 2′-5′ oligoadenylate synthetase and Mx proteins, which promote viral RNA breakdown and impede viral multiplication, may be involved in this improvement.
Inflammation
It is also believed that Selank may have anti-inflammatory properties that might help with infection management. While inflammatory reactions are essential for eliminating pathogens, they risk tissue harm if left unchecked. Findings imply that Selank’s regulation of inflammatory pathways might lend influence in balancing the immune response to reduce excessive inflammation while maintaining efficient pathogen clearance.
Inflammatory Routes
Selank has been theorised to affect important processes involved in inflammation, such as the NF-κB pathway, which controls cytokine production that promotes inflammation. There is a theoretical possibility that Selank might lessen inflammation-induced damage by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6 by modifying NF-κB activity.
Inflammatory Injury
The peptide’s alleged anti-inflammatory potential may spare tissues from infection-related harm. Selank appears to improve outcomes in inflammation caused by infections by lowering the infiltration of inflammatory cells and generating reactive oxygen species. This might help maintain the integrity and function of tissues.
Mechanisms of Autoimmunity
Neuroimmune interactions may mediate at least some of Selank’s impact on the immune system. Because of the two-way flow of information between the CNS and the immune system, the peptide’s impacts on the CNS are theorised to indirectly affect immunological function.
The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Correlation
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis may play a role in this process since it controls immune function and stress responses. Selank’s modulation of HPA axis activity has been hypothesised to change glucocorticoid’s immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory impacts. In theory, this regulation may improve the immune system’s capacity to deal with the stress and inflammation caused by infections.
Neurotransmitter Networks
One possible explanation for Selank’s immunomodulatory actions is its interaction with neurotransmitter systems. Since these neurotransmitters may affect the activity of immune cells and the generation of cytokines, Selank’s neuromodulatory potential may impact immunological responses to infections.
Concluding Remarks
Further empirical data is needed to confirm the potential involvement of Selank in modifying immunological responses and infection management, but its theoretical and speculative processes suggest promise in these areas. Thorough investigations to confirm Selank’s effectiveness and potential in infection situations and the exact biochemical mechanisms by which it functions should be the focus of future studies. To fully realise Selank’s promise in infection control, it is necessary to understand these processes. Only then can new approaches be considered.
Scientists interested in research peptides for sale are encouraged to visit the Core Peptides website for the highest-quality, most affordable research compounds.
References
[i] Leonidovna YA, Aleksandrovna SM, Aleksandrovna TA, Aleksandrovna BO, Fedorovich MN, Aleksandrovna AL. The Influence of Selank on the Level of Cytokines Under the Conditions of “Social” Stress. Curr Rev Clin Exp Pharmacol. 2021;16(2):162-167. doi: 10.2174/1574884715666200704152810. PMID: 32621722.
[ii] Panikratova YR, Lebedeva IS, Sokolov OY, Rumshiskaya AD, Kupriyanov DA, Kost NV, Myasoedov NF. Functional Connectomic Approach to Studying Selank and Semax Effects. Dokl Biol Sci. 2020 Jan;490(1):9-11. doi: 10.1134/S001249662001007X. Epub 2020 Apr 27. PMID: 32342318.
[iii] Vyunova TV, Andreeva L, Shevchenko K, Myasoedov N. Peptide-based Anxiolytics: The Molecular Aspects of Heptapeptide Selank Biological Activity. Protein Pept Lett. 2018;25(10):914-923. doi: 10.2174/0929866525666180925144642. PMID: 30255741.
[iv] Povarov IS, Kondratenko RV, Derevyagin VI, Myasoedov NF, Skrebitsky VG. Effect of Selank on Spontaneous Synaptic Activity of Rat Hippocampal CA1 Neurons. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2017 Mar;162(5):640-642. doi: 10.1007/s10517-017-3676-3. Epub 2017 Mar 30. PMID: 28361410.
[v] Fomenko EV, Bobyntsev II, Kryukov AA, Ivanov AV, Andreeva LA, Myasoedov NF. Effect of Selank on Functional State of Rat Hepatocytes under Conditions of Restraint Stress. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2017 Aug;163(4):415-418. doi: 10.1007/s10517-017-3817-8. Epub 2017 Aug 29. PMID: 28853100.
Latest Thailand News
Follow The Thaiger on Google News: