Deforestation in Thailand: challenges and solutions for forest conservation

Thailand is currently facing a significant environmental challenge that has garnered widespread concern, particularly among conservationists: deforestation. This issue is more severe in Thailand than in many other Southeast Asian countries, primarily due to the rapid clearance of forests to accommodate agricultural expansion necessitated by population growth and the country’s focus on exporting agricultural products.
Furthermore, the logging industry and the demand for fuelwood significantly contribute to the reduction of forested areas. This situation has raised alarms not only among environmentalists but also among those assessing the severity of these activities on Thailand’s ecological balance. Importantly, the methodologies employed to evaluate forest degradation play a crucial role in accurately understanding the magnitude of this crisis.
History of Thai forest management
The management of forests in Thailand has undergone a significantly fluctuating journey. It commenced with the establishment of the Royal Forest Department in the late 19th century, marking Thailand’s initial concerted effort towards forest conservation and ensuring its longevity.
A pivotal strategy implemented was the prohibition of logging within natural forests several decades ago. This measure aimed at halting further loss of flora and fauna, essentially drawing a line against ongoing deforestation. Additionally, Thailand embarked on initiatives such as reforestation and the designation of protected areas as remedial actions towards mitigating environmental degradation.
An innovative approach adopted involves Buddhist leaders ordaining trees; this not only integrates spiritual practices but also serves as an ingenious method to foster a change in perception regarding indiscriminate tree felling. This synergy between faith and environmental activism has ignited further discussions on the imperative to preserve forests for future generations.
However, challenges persist, with incidences of illicit tree cutting and conversion of forested land into agricultural use continuing to pose threats to conservation efforts. Despite these obstacles, there is an emerging collective determination among government entities, environmental advocates, and local communities aimed at devising effective strategies for sustainable forest management that include all stakeholders.
These varied experiences highlight Thailand’s ongoing endeavour to enhance its management of green spaces, recovering from significant setbacks while exploring inclusive methods to ensure the flourishing of its natural environments. Achieving a harmonious balance between economic development and environmental preservation remains a formidable challenge, yet there is evident commitment towards striving for optimal outcomes in this regard.
Causes of deforestation in Thailand
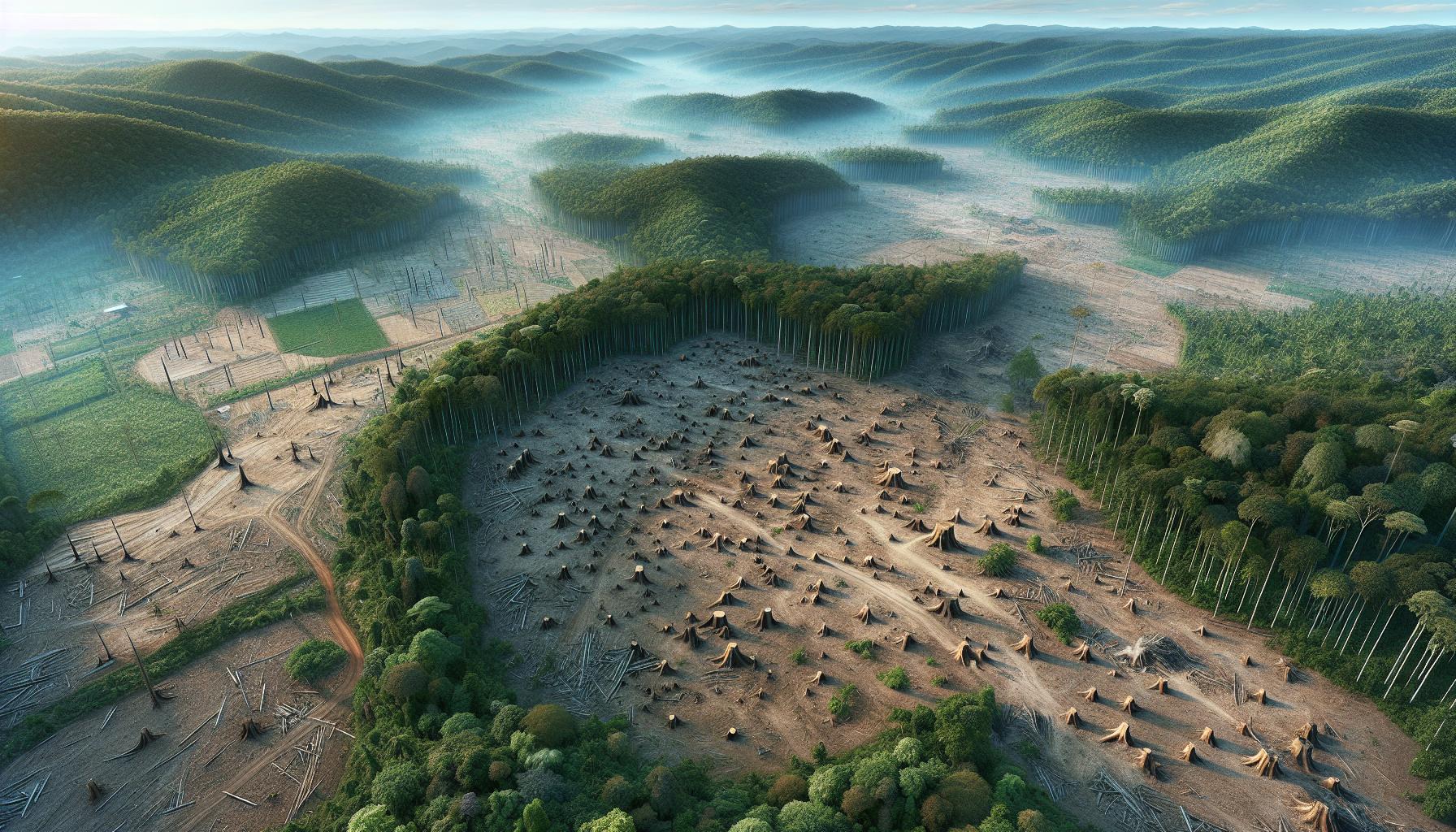

Population Growth
As Thailand’s population increases, there is a heightened demand for forest resources. This demand arises from the need for housing, agriculture, and infrastructure. Consequently, deforestation occurs to accommodate agricultural expansion, residential areas, and transportation networks. The correlation between population growth and the conversion of forest lands into rice paddies and sugar cane fields exemplifies the significant impact of human expansion on natural environments.
Agricultural Policy
In the context of agricultural policies in Thailand, there has been a significant emphasis on the cultivation of cash crops, which include plants with global market demand such as rubber and palm oil. The expansion of these crops necessitates extensive land use. This space is predominantly sourced from forested areas. While such policies have contributed to economic growth in Thailand, they come at a considerable cost to the environment, resulting in diminished biodiversity and reduced forest cover.
Land Ownership Policy
The issue of land ownership regulations in Thailand has significantly contributed to the depletion of forested areas. The failure to address ambiguities surrounding land claims and the authorization for their use has allowed certain individuals to exploit these oversights. Consequently, they acquire more land than likely anticipated for financial gain. This exploitation of legal loopholes has led to the destruction of verdant spaces as they are cleared for commercial and private developments, exacerbating the deforestation crisis.
Illegal Logging
Thailand is confronted with a significant challenge in combating illegal logging, which persistently diminishes its forests despite widespread recognition of the detrimental effects. In an effort to address this issue, Thailand implemented a comprehensive ban on logging in 1989. However, this measure has not effectively curtailed unauthorised operations due to the lucrative nature of the timber market. The ramifications of such illicit activities extend beyond mere deforestation; they disrupt entire ecosystems and have potential long-term financial and environmental consequences. A concerted effort involving law enforcement enhancement and community engagement is essential for the preservation of our forests.
In addressing the critical issue of preventing Thailand’s forests from becoming barren landscapes, achieving equilibrium is paramount. It is crucial to identify a strategy that harmonises economic pursuits with environmental sustainability. By adopting stricter measures against illegal logging, revising agricultural practices, and planning urban development with greater consideration for ecological preservation, there exists potential to mitigate deforestation and safeguard the verdant areas upon which we all rely.
Impacts of deforestation in Thailand
The video above is from tutor2u, YouTube channel.
Biodiversity Loss
Did you know that the forests of Thailand serve as an extensive and vital habitat for a diverse range of animal species? However, these critical habitats are facing rapid depletion due to deforestation. The primary issue arises when these forests are fragmented, disrupting the ecosystem and placing numerous species in jeopardy. Even within areas designated as wildlife sanctuaries, challenges persist. Infrastructure developments, such as roads and buildings, facilitate illegal hunting activities. Consequently, many species that once thrived in these regions are at risk of extinction unless significant conservation efforts are implemented promptly. This situation undeniably calls for urgent attention.
Habitat Destruction
Therefore, when forests are cleared to make space for agricultural developments, urban expansion, and infrastructure projects, significant disruption occurs to vital habitats for wildlife. Moreover, this action interferes with natural processes such as carbon sequestration and water regulation. Additionally, the encroachment of farming activities into higher elevations due to lenient regulations exacerbates the adverse effects on remaining forests and their inhabitants. In essence, the destruction of natural habitats can be likened to a cascading series of events—affecting biodiversity profoundly and diminishing the environment’s resilience.
Local Communities
The destruction of forests is not merely about the loss of trees; it significantly disrupts human lives, particularly for indigenous populations and individuals reliant on these ecosystems for their livelihood. An illustrative case is that of the Karen community within Kaeng Krachan National Park. Their existence is being profoundly affected as they are displaced and embroiled in disputes over land ownership. This scenario exemplifies how deforestation can drastically alter human conditions. It is imperative for governments to intervene and provide resolutions that preserve natural habitats while concurrently ensuring the welfare of these communities. Collaboration is essential; it must be ensured that these individuals have a secure place to reside while maintaining the health and integrity of our environmental resources.
Climate Change
Deforestation in Thailand transcends a mere reduction in tree numbers; it significantly disrupts climatic conditions due to the diminished capacity of forests to absorb CO2. This exacerbation of the greenhouse effect contributes to increased temperatures, irregular precipitation patterns, and a variety of extreme weather phenomena. Furthermore, converting forests into agricultural lands or urban areas serves as a catalyst for substantial carbon emissions. Consequently, it is imperative for Thailand to devise and implement a comprehensive strategy to address these climate change challenges effectively.
Reforestation
Thailand is embarking on a critical mission to fundamentally transform its approach to forest conservation. The strategy involves adopting sophisticated land management practices and ensuring the participation of local communities. The primary objective is to protect the nation’s diverse flora and fauna while simultaneously improving the living conditions of its inhabitants without compromising the integrity of natural ecosystems. This initiative seeks to strike a delicate balance between economic development and environmental sustainability. Through meticulous planning and a steadfast commitment to preserving nature, Thailand aims to become a leading figure in forest conservation efforts. This endeavour is not solely focused on addressing current challenges but is also committed to ensuring the long-term well-being of future generations.
If you are still looking for more green practices, you may check out our article, ‘Zero waste living in Thailand.‘
Latest Thailand News
Follow The Thaiger on Google News: