Thailand acknowledges wildlife markets could be dangerous to humans
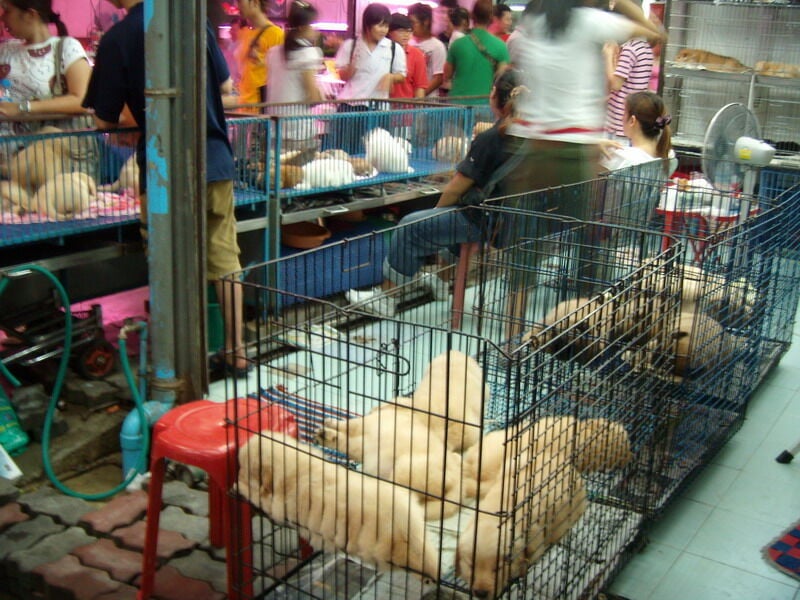

The Thai Ministry of Public Health is being praised after seemingly doing an about face over whether Bangkok’s Chatuchak Weekend Market could be the source of Covid‐19. After health officials denied that the World Health Organisation was investigating the market, a recent Facebook live press conference saw the Ministry acknowledging that wildlife trades may endanger public health.
The recent investigation by the WHO of Wuhan, the province in China where Covid19 is thought to have originated, has concluded that the virus most likely did not come from a laboratory, and instead, came from animals supplied by Chinese wildlife breeding farms, or from infected animals traded somewhere in Southeast Asia. As Chatuchak Market is arguably the region’s largest illegal wildlife trade market, a Danish virologist on the WHO investigation team pointed towards the Bangkok market as a potential source of the Covid19 virus.
Now, the Thai Ministry of Public Health is going to collaborate with the Ministry of Environment and its Department of National Parks to closely inspect Chatuchak market, and roll out a joint plan to increase wildlife protection and stop the wild animal trade in markets.
Southeast Asia has historically supplied most of China’s wildlife trade, which the virologist sees as worrisome. As commercially traded animals can carry pathogens that could compromise a human’s immune system. For example, in 2019, zebras that were legally imported into Thailand, carried a small fly species that jumped to local horses, causing African Horse Sickness. The mortality rate was over 90%, causing over 600 horse deaths.
Some animals are especially susceptible to viruses hosted by bats, such as the SARS virus. That virus jumped from a civet cat that was infected by a bat. Other viruses that are thought to have jumped from bats to other animals include rabies and Ebola. Minks and Pangolins have also been discovered to carry a coronavirus and are still being commercially traded in Southeast Asia today.
In a spotcheck carried out by Freeland, a global nonprofit organisation, Chatuchak Market is still selling ferrets, coati, civets, polecats, mongoose, raccoons, meerkats, scarlet macaws, capybara, african gray parrots, cougars, multiple species of turtles, snakes, rodents and lizards from Latin America, Africa and Australia.
SOURCE: Freeland
Latest Thailand News
Follow The Thaiger on Google News: